 Image credit by Yu Zhong
Image credit by Yu Zhong
Abstract
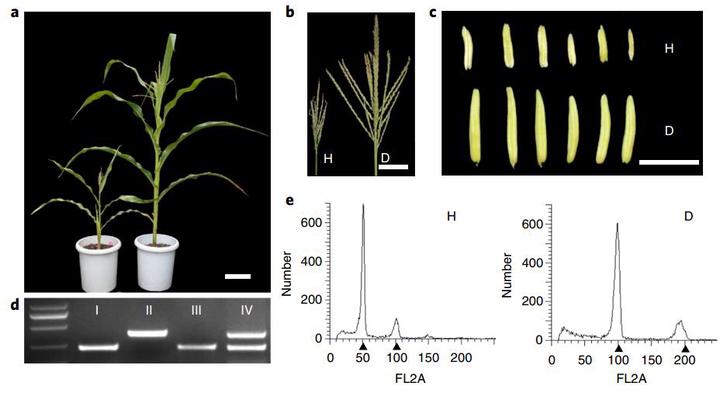
Doubled haploid (DH) breeding based on in vivo haploid induction has led to a new approach for maize breeding. All modern haploid inducers used in DH breeding are derived from the haploid inducer line Stock6. Two key quantitative trait loci, qhir1 and qhir8, lead to high-frequency haploid induction. Mutation of the gene MTL/ZmPLA1/NLD in qhir1 could generate a ~2% haploid induction rate (HIR); nevertheless, this mutation is insufficient for modern haploid inducers whose average HIR is ~10%6. Therefore, cloning of the gene underlying qhir8 is important for illuminating the genetic basis of haploid induction. Here, we present the discovery that mutation of a non-Stock6-originating gene in qhir8, namely, ZmDMP, enhances and triggers haploid induction. ZmDMP was identified by map-based cloning and further verified by CRISPR–Cas9-mediated knockout experiments. A single-nucleotide change in ZmDMP leads to a 2–3-fold increase in the HIR. ZmDMP knockout triggered haploid induction with a HIR of 0.1–0.3% and exhibited a greater ability to increase the HIR by 5–6-fold in the presence of mtl/zmpla1/nld. ZmDMP was highly expressed during the late stage of pollen development and localized to the plasma membrane. These findings provide important approaches for studying the molecular mechanism of haploid induction and improving DH breeding efficiency in maize.